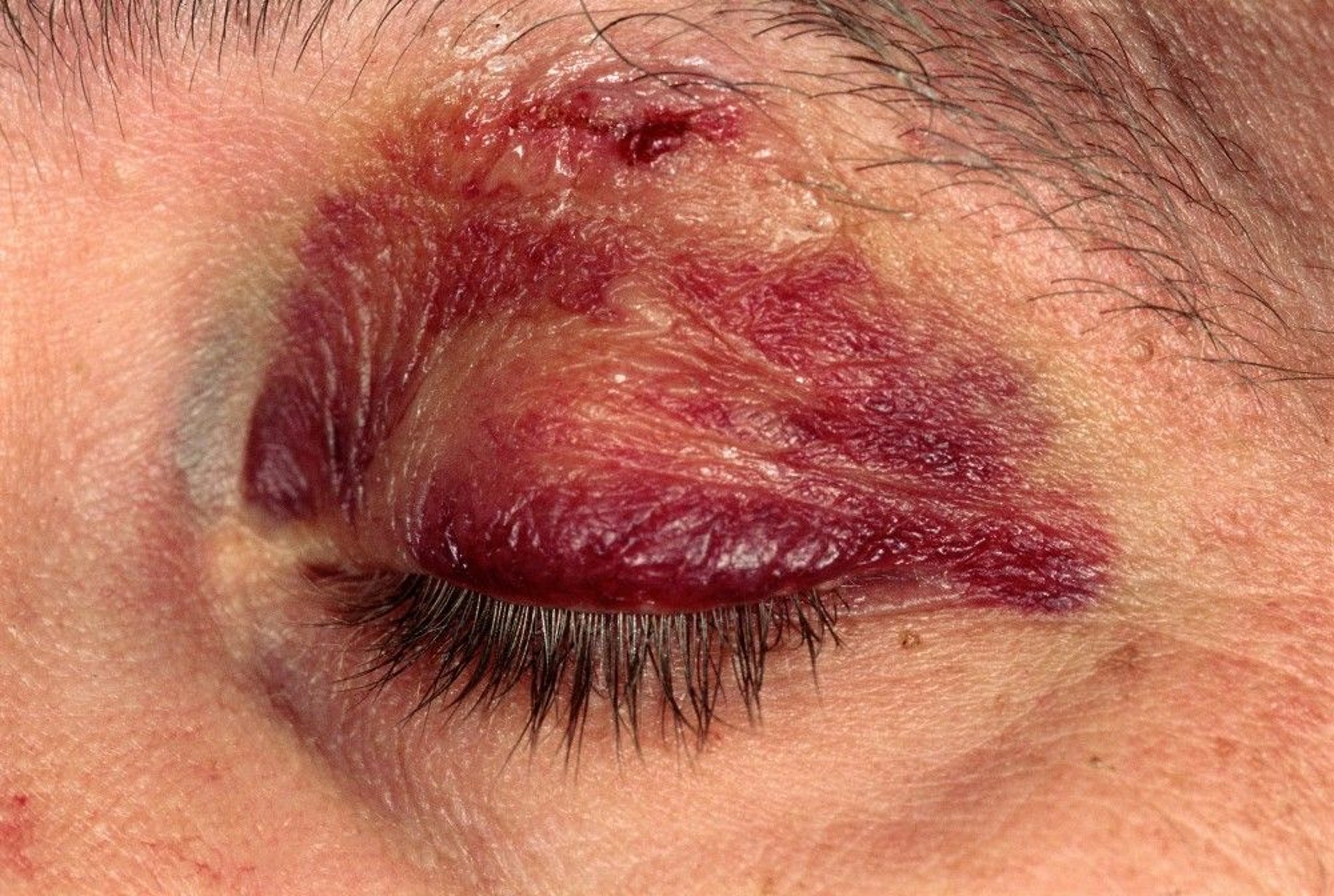
In the first 24 hours after a blunt eye injury, blood may leak into the skin of the eyelid and surrounding areas, causing swelling and a bruise (contusion), commonly called a black eye.
Topic Resources
(See also Overview of Eye Injuries.)
The blood usually drains toward the bottom of the eyelid after 1 or 2 days, resulting in swelling and discoloration just below the lower eyelid. Black eyes themselves usually have no effect on vision as long as the bleeding remains superficially within the lids, although other eye injuries that accompany them may be serious. On occasion, bleeding may affect the deeper structures in the orbit (eye socket), and if the orbital hemorrhage is severe, it may permanently damage the optic nerve.
SCOTT CAMAZINE/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Black eyes resolve without treatment after a few days or weeks. During the first 24 to 48 hours, ice packs may help reduce swelling and ease the pain of a black eye.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as aspirin or ibuprofen) or acetaminophen can be given if the pain is significant. However, people who have bleeding within the eye should probably use Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as aspirin or ibuprofen) or acetaminophen can be given if the pain is significant. However, people who have bleeding within the eye should probably useacetaminophen and not use NSAIDs, which may worsen bleeding.
If a person has severe eyeball pain or vision problems (for example, blurry or double vision), the doctor will further examine the eye for lacerations (cuts), fractures, or bleeding into the eye socket.