Topic Resources
Melanin is the pigment that produces the various shades and colors of human skin, hair, and eyes. Coloration (pigmentation) is determined by the amount of melanin in the skin. Without melanin, the skin would be pale white with shades of pink caused by blood flow through the skin.
People with fair skin produce very little melanin, people with dark skin produce moderate amounts, and people with very dark skin produce the most. People with albinism have little or no melanin and thus their skin appears white or pale pink.
Usually, melanin is fairly evenly distributed in the skin, but sometimes people have spots or patches of skin with more melanin. Examples of such spots include freckles, age spots (lentigines), and melasma.
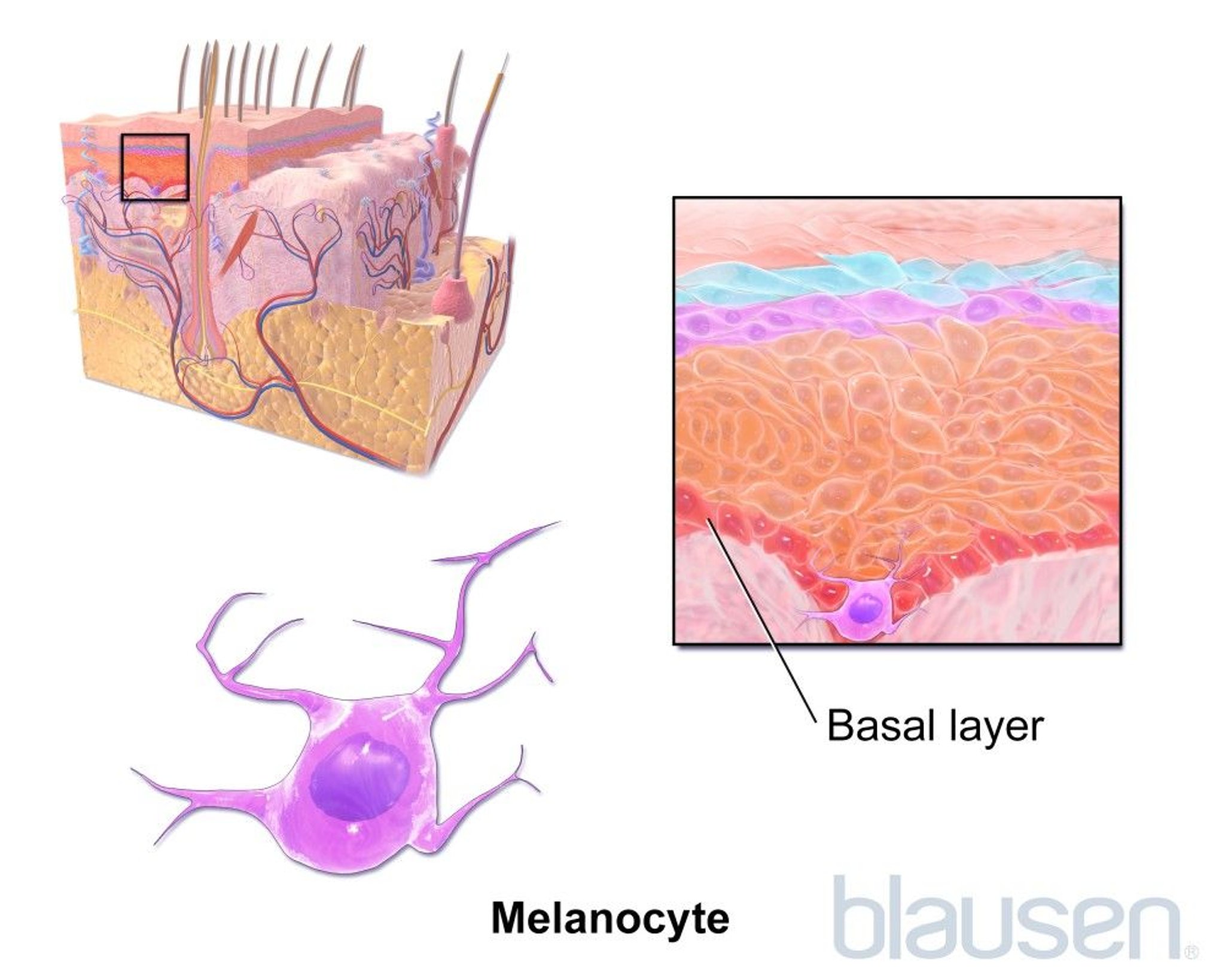
Melanin is produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. Melanocytes are scattered among other cells in the deepest layer of the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) called the basal layer. After melanin is produced, it spreads into other nearby skin cells.
Pigment disorders
Pigment disorders can be widespread and affect many areas of skin, or they can be localized and affect only certain areas of the skin. The pigmentation changes they cause are called
Depigmentation
Hypopigmentation
Hyperpigmentation
Depigmentation is complete loss of pigment. The skin is white. Widespread depigmentation occurs in vitiligo.
Hypopigmentation is an abnormally low amount of melanin. The skin is lighter in color than normal (for example, lighter than in areas of skin that are not affected). Widespread hypopigmentation of the skin occurs in albinism. Hypopigmentation can also be caused by
Previous injury to the skin, such as a blister, ulcer, burn, exposure to a chemical, or skin infection
Inflammatory conditions of the skin that have healed (such as atopic dermatitis or psoriasis)
Rare hereditary conditions
Hyperpigmentation is usually caused by an abnormally high amount of melanin, but sometimes it is caused by deposition of other pigmented substances that are not normally present in the skin. The skin is darker in color and sometimes is a different color than skin in unaffected areas. Hyperpigmentation can be caused by
Disorders that cause inflammation
Medications or substances
Exposure to sunlight
Cancer