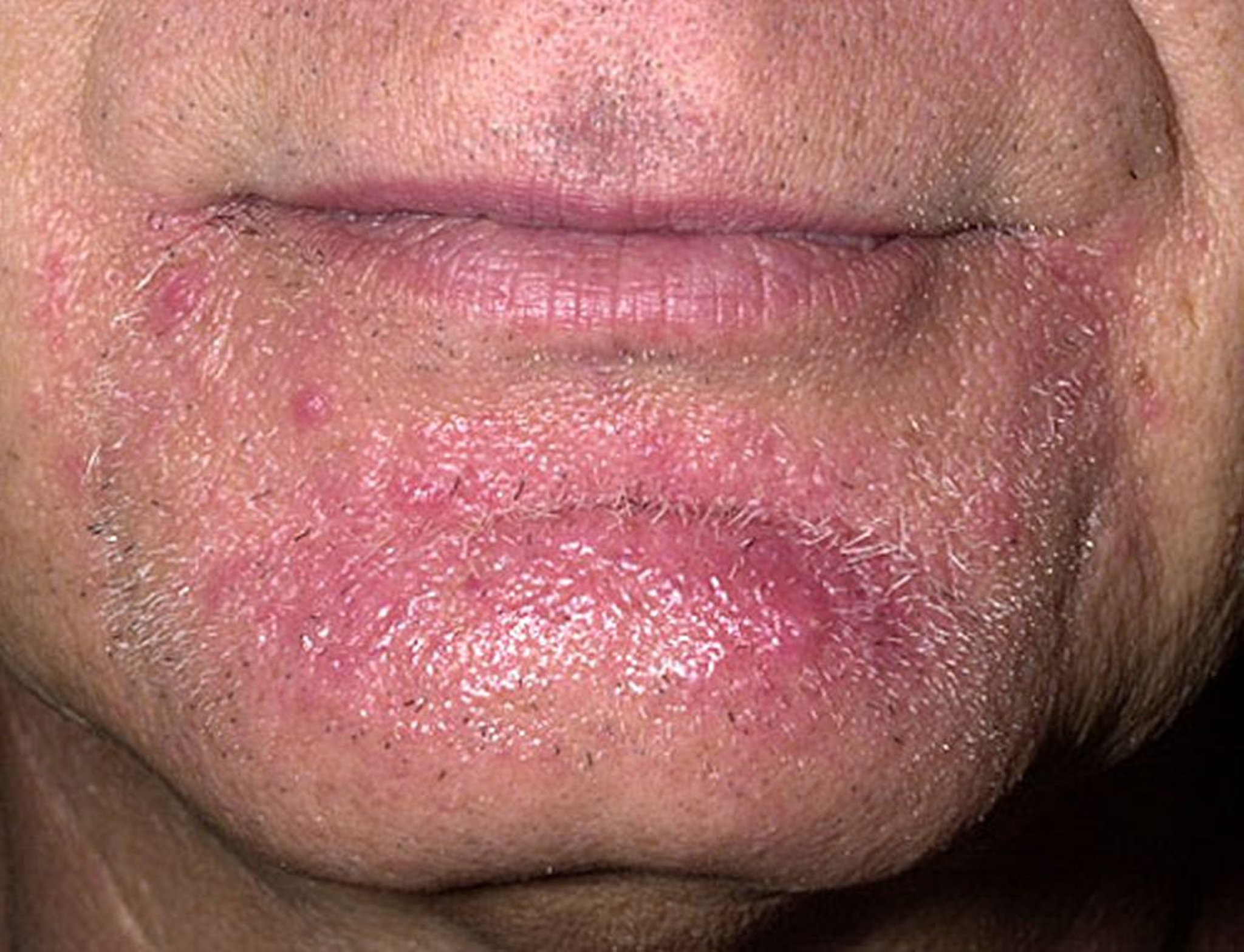
Tinea barbae is a dermatophyte infection of the beard area most often caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes or T. verrucosum. Diagnosis is by examination of plucked hairs on potassium hydroxide wet mount. Treatment is with oral antifungals and sometimes prednisone.
Topic Resources
Image provided by Thomas Habif, MD.
Tinea barbae is a dermatophytosis that manifests in the beard area as superficial annular lesions, but deeper infection similar to folliculitis may occur. Tinea barbae may also manifest as a kerion (a large, boggy nodule caused by a severe inflammatory reaction to the dermatophyte) that can result in scarring hair loss.
Diagnosis of Tinea Barbae
Potassium hydroxide wet mount
Diagnosis of tinea barbae is by identifying the fungal element (hyphae) on potassium hydroxide wet mount of plucked hairs, culture, or biopsy.
Differential diagnosis of follicular-based papules and pustules in the beard area includes bacterial folliculitis.
Treatment of Tinea Barbae
Oral antifungals
Sometimes prednisone
Treatment of tinea barbae is micronized griseofulvin 500 mg to 1 g orally once a day until 2 to 3 weeks after clinical clearance (see table Treatment of tinea barbae is micronized griseofulvin 500 mg to 1 g orally once a day until 2 to 3 weeks after clinical clearance (see tableOptions for Treatment of Superficial Fungal Infections). Terbinafine 250 mg orally once a day and itraconazole 200 mg orally once a day have also been used. ). Terbinafine 250 mg orally once a day and itraconazole 200 mg orally once a day have also been used.
If the lesions are severely inflamed, a short course of prednisone should be added (to lessen symptoms and perhaps reduce the chance of scarring), starting with 40 mg orally once a day (for adults) and tapering the dose over 2 weeks.If the lesions are severely inflamed, a short course of prednisone should be added (to lessen symptoms and perhaps reduce the chance of scarring), starting with 40 mg orally once a day (for adults) and tapering the dose over 2 weeks.