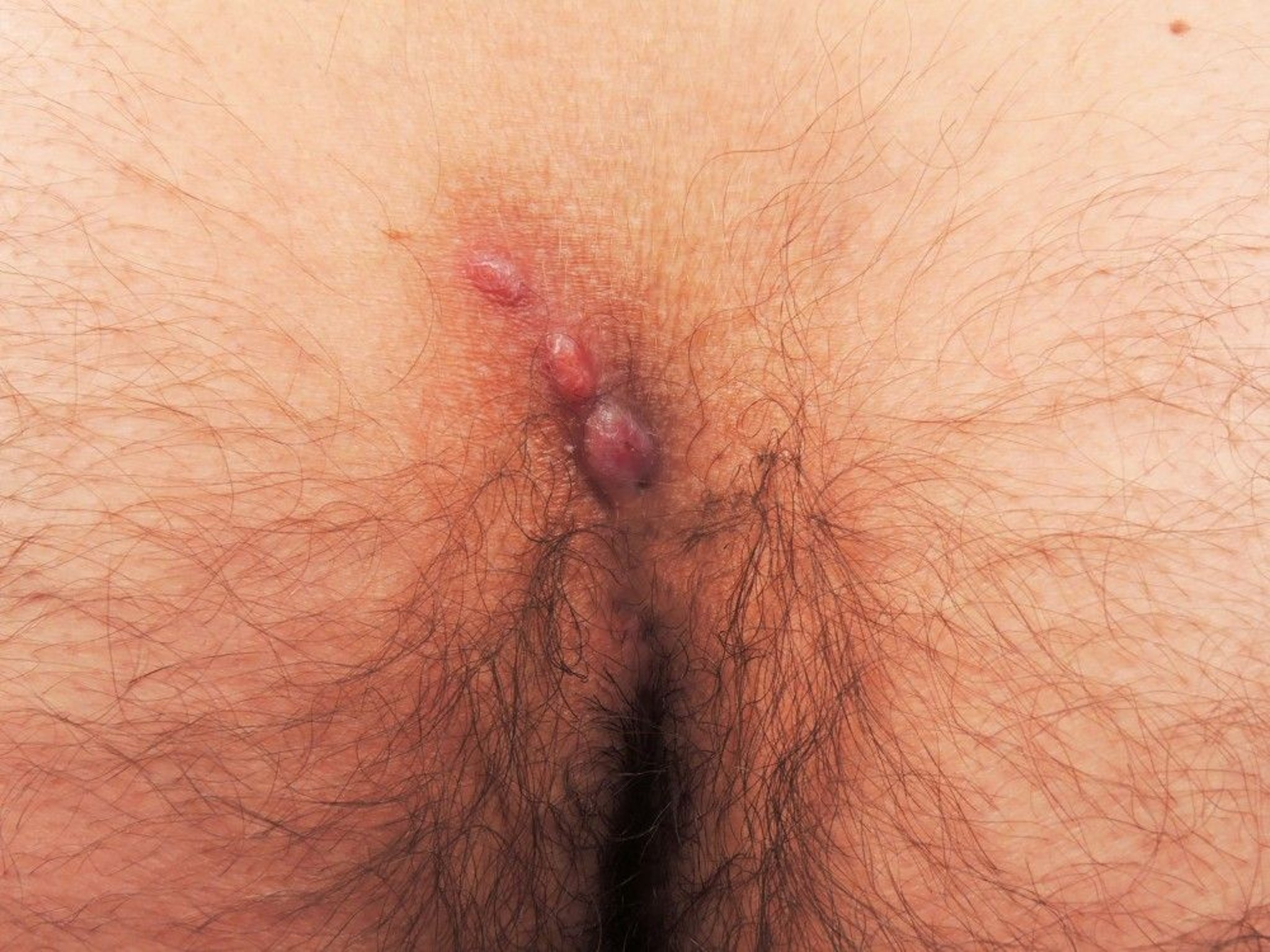
Pilonidal disease refers to an acute abscess or chronic draining sinus in the sacrococcygeal area.
Topic Resources
(See also Evaluation of Anorectal Disorders.)
IRAND/BSIP/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Pilonidal disease usually occurs in young, hirsute, White males but can also occur in females.
One or several midline or adjacent-to-the-midline pits or sinuses occur in the skin of the sacral region and may form a cavity (cyst), often containing hair. The lesion is usually asymptomatic; infected lesions (abscesses) are painful. When the abscess drains to the skin it is called a pilonidal sinus, and might intermittently drain.
Treatment of Pilonidal Disease
For abscesses, incision and drainage
For sinuses and cysts, extirpation and closure
Treatment of an acute abscess is by incision and drainage (1).
Usually, one or more chronic draining sinuses persist and must be extirpated by excision and primary closure or by an open technique (eg, cystotomy, marsupialization) (1). Minimally invasive techniques that use endoscopic or video assistance have also been used with some success but require specialized equipment and expertise. Antibiotics are typically not needed with pilonidal disease surgery, but should be considered on an individual case basis.
Larger cysts may require a rotation flap to close the defect (1).
Treatment reference
1. Johnson EK, Vogel JD, Cowan ML, Feingold DL, Steele SR. Clinical Practice Guidelines Committee of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons' Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Pilonidal Disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 2019;62(2):146-157. doi:10.1097/DCR.0000000000001237