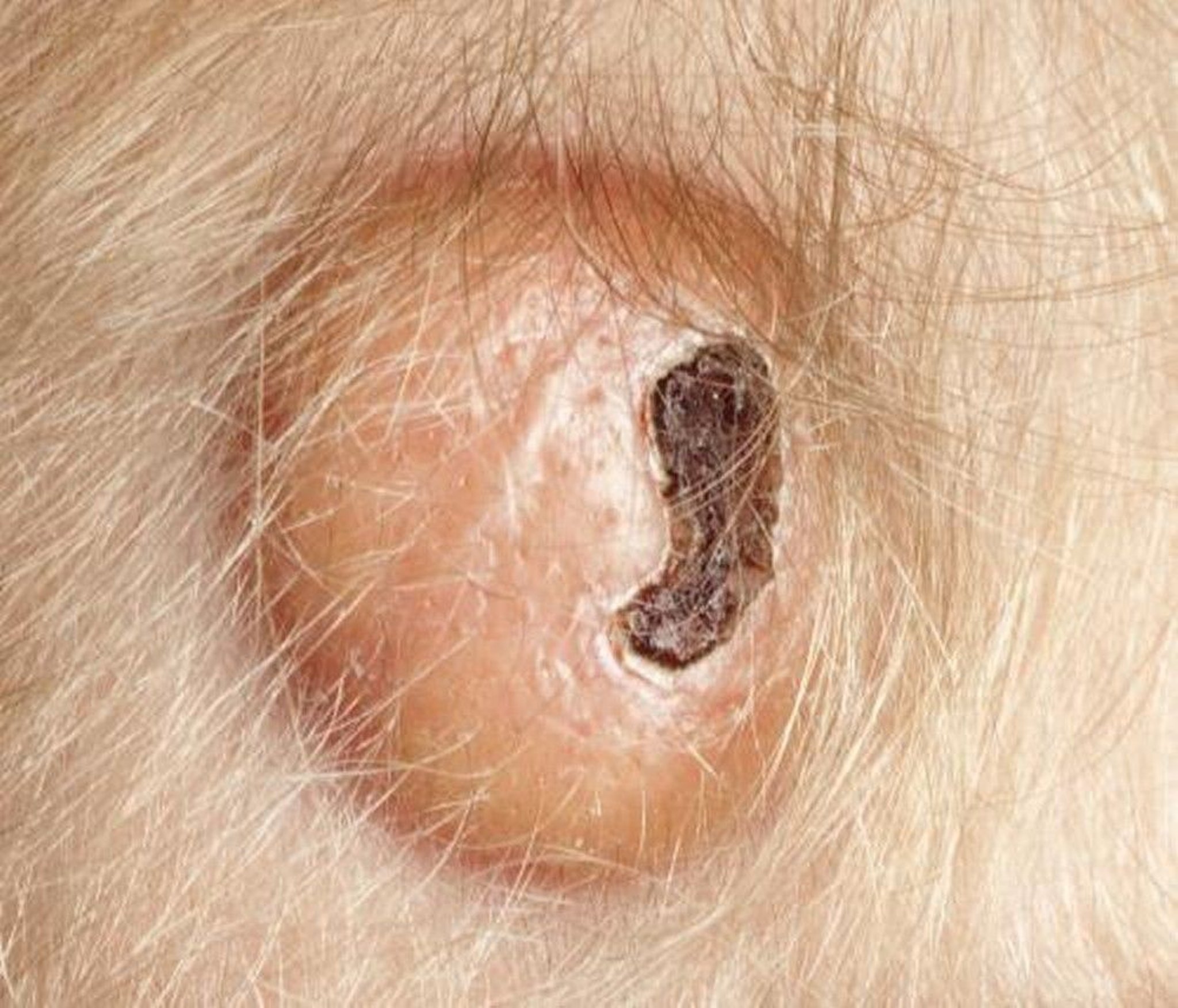
Juvenile xanthogranuloma is a dendritic cell-related histiocytic syndrome that usually affects only the skin, causing single or multiple lesions, which can resolve spontaneously.
Topic Resources
Systemic involvement can occur, causing visceral organ lesions, involving the liver, lungs, and/or bone marrow.
Juvenile xanthogranuloma is rarely associated with neurofibromatosis and/or juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia
Topical corticosteroids or sirolimus can be used to treat skin lesions. Systemic lesions are treated with chemotherapy similar to what is used in Topical corticosteroids or sirolimus can be used to treat skin lesions. Systemic lesions are treated with chemotherapy similar to what is used inLangerhans cell histiocytosis. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway mutations have been identified, so targeted therapy can also be used.
MID ESSEX HOSPITAL SERVICES NHS TRUST/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY