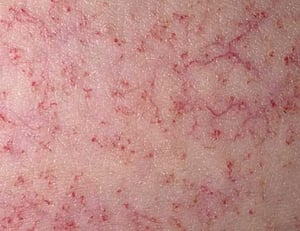
Idiopathic telangiectasias are fine, dilated intracutaneous veins that are not clinically significant but may be extensive and unsightly.
Topic Resources
Telangiectasias are small, dilated blood vessels; they are most often idiopathic.
Photo provided by Thomas Habif, MD.
Although telangiectasias are usually asymptomatic, many people consider even the smallest telangiectasias cosmetically unacceptable.
© Springer Science+Business Media
Telangiectasias (spider veins) are usually asymptomatic. However, some patients report a burning sensation or pain, and many people consider even the smallest telangiectasias cosmetically unacceptable.
Diagnosis is clinical.
Treatment of Idiopathic Telangiectasias
Sclerotherapy
Laser treatment
Telangiectasias can usually be eliminated by sclerotherapy, intracapillary injections of 0.3% solution of sodium tetradecyl sulfate through a fine-bore needle. Hypertonic saline 23.4% is sometimes used but causes fairly severe, temporary, localized pain; therefore, large areas of telangiectasias may require several treatments. Pigmentation may develop but usually subsides, often completely. Skin ulceration may result if the injection is extravascular or too large. Telangiectasias can usually be eliminated by sclerotherapy, intracapillary injections of 0.3% solution of sodium tetradecyl sulfate through a fine-bore needle. Hypertonic saline 23.4% is sometimes used but causes fairly severe, temporary, localized pain; therefore, large areas of telangiectasias may require several treatments. Pigmentation may develop but usually subsides, often completely. Skin ulceration may result if the injection is extravascular or too large.
Laser treatment is effective, but large areas require several treatments. Small telangiectasias may persist or recur after initial treatment.